Part 2 - A simple genetic algorithm in Python
We will look at how a genetic algorithm can be used to find the minimum of a function and implement it in Python.
Some definitions
A genetic algorithm is an optimisation heuristic inspired from the mechanism of Darwin’s natural evolution. It leverages the process of natural selection to select individuals that are fittest to survive to the next generation.
- Individual (= chromosome): one possible solution to the problem
- Design parameters (= genes): the parameters to optimise. Each individual is defined by a list of its design parameters.
- Population: a group of individuals or designs to be optimised
- Generation: a population at a specific interation
- Objective function (= fitness function): the function to minimise
- Design space: set of all the possible design parameters values
- Objective space: set of all the objective function value
- Parents: individuals belonging to an older generation
- Offspring: individual belonging to a younger generation
- Crossover: it consists in combining the genes of two parents to create an offspring.
- Mutation: it consists in altering a few genes of a parent to create an offspring.
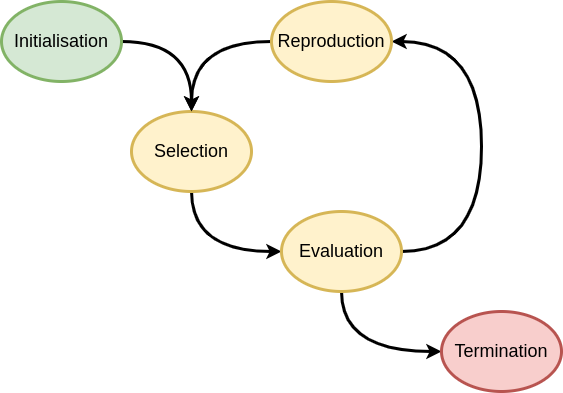
In its most basic form, a genetic algorithm comprises the following stages:
- Initialisation of the population
- Selection of the best parents
- Reproduction (by mutation and/or by crossover) to generate offsprings
- Evaluation of the population
- Termination according to criterion
Implementation
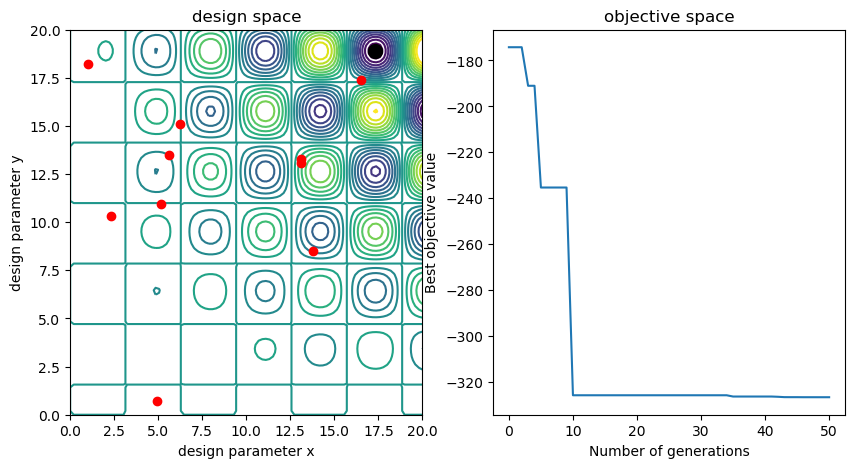
We will implement a simple genetic algorithm in Python. The objective is to find the minimum of this objective function with 2 design parameters: \(Z(x, y) = x\sin(x)*y\cos(y)\). The source code can be found here.


Leave a comment